Scientific Notation
What Is Scientific Notation?
Sometimes scientific calculations result in very large numbers, like 918,700,000,000,000,
or in very small numbers, such as 0.0000000578. Scientific notation is a short way of
representing such numbers without writing the place-holding zeros. In scientific notation,
we write the number as a product of two factors: the first is a number between 1
and 10, and the second is a power of ten, written as 10exponent.
PROCEDURE: To write a number in scientific notation, first identify which digits
are not place-holding zeros. Then place the decimal point after the leftmost
digit. To find the exponent for the factor of 10, count the number of places that
you moved the decimal point. If you moved the decimal point to the left, the
exponent will be positive. If you moved the decimal point to the right, the
exponent will be negative.
SAMPLE PROBLEM: Write 653,000,000 in scientific notation.
|
Step 1: Identify the number without the
place-holding zeros.
653 |
Step 2: Place the decimal point
after the leftmost digit.
6.53 |
|
Step 3: Find the exponent by counting the
number of places that you moved the decimal
point.
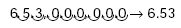
The decimal point was moved 8 places to the
left. Therefore, the exponent of 10 is positive
8. Remember, if the decimal point had moved
to the right, the exponent would be negative.
|
Step 4: Write the number in
scientific notation.
6.53 × 108 |
|