Real Numbers and the Real Line
Real numbers can be represented by a coordinate system called the real line or x-axis. The real number corresponding to a point on the real line is the
coordinate of the point. As the figure below shows, it is customary to identify those points
whose coordinates are integers.
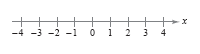
The point on the real line corresponding to zero is the origin and is denoted by 0.
The positive direction (to the right) is denoted by an arrowhead and is the direction
of increasing values of x. Numbers to the right of the origin are positive. Numbers to
the left of the origin are negative. The term nonnegative describes a number that is
positive or zero. The term nonpositive describes a number that is negative or zero.
Each point on the real line corresponds to one and only one real number, and each
real number corresponds to one and only one point on the real line. This type of
relationship is called a one-to-one-correspondence.
Each of the four points in the figure below corresponds to a rational number—one
that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers. (Note that
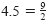 and and
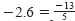 .)
Rational numbers can be represented either by terminating decimals
such as .)
Rational numbers can be represented either by terminating decimals
such as
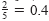 or by repeating decimals such
as or by repeating decimals such
as
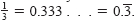
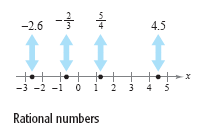
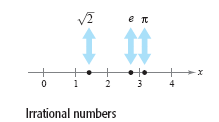
Real numbers that are not rational are irrational. Irrational numbers cannot be
represented as terminating or repeating decimals. In computations, irrational numbers
are represented by decimal approximations. Here are three familiar examples.

See figure below.
 |